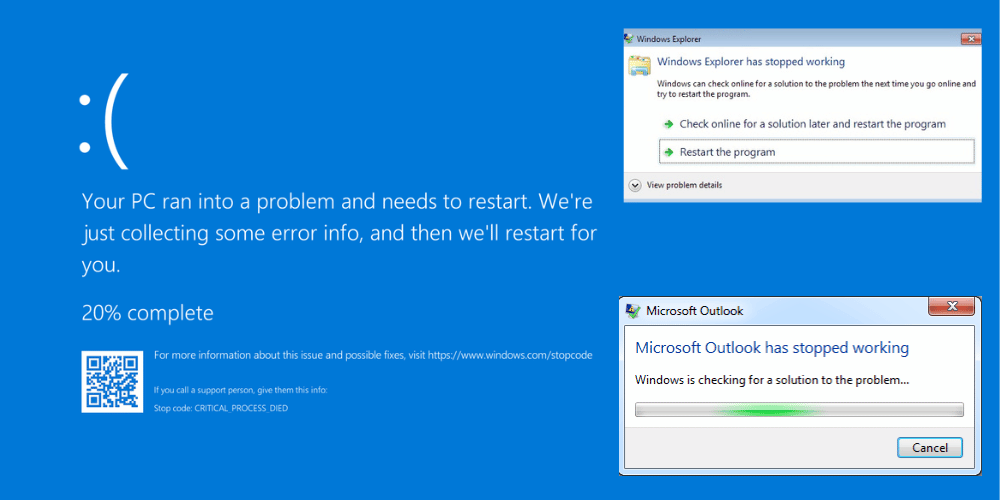
In today’s fast-paced digital world, encountering technical issues on your computer can be incredibly frustrating. Whether it’s a persistent problem with Windows Explorer, an Outlook application that keeps crashing, or the dreaded Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), these disruptions can significantly impact your productivity and peace of mind.
Have you ever experienced any of these scenarios? You’re in the middle of an important task, and suddenly, Windows Explorer crashes without warning. Or perhaps you’re trying to send an urgent email, and Outlook decides to freeze and shut down repeatedly. Worse still, your computer might abruptly display the infamous Blue Screen of Death, leaving you scrambling to understand what went wrong and how to fix it.
This blog is here to help. We’ll dive deep into the common causes behind these frustrating issues and provide you with comprehensive, step-by-step solutions to resolve them. From simple troubleshooting tips to advanced fixes, we’ve got you covered. Our aim is to equip you with the knowledge and tools to not only fix these problems but also prevent them from recurring in the future.
Stay with us as we explore effective strategies to tackle Windows Explorer crashes, stabilize your Outlook application, and conquer the Blue Screen of Death once and for all. Let’s turn these tech troubles into triumphs!
Table of contents
2. Windows Explorer Keeps Crashing
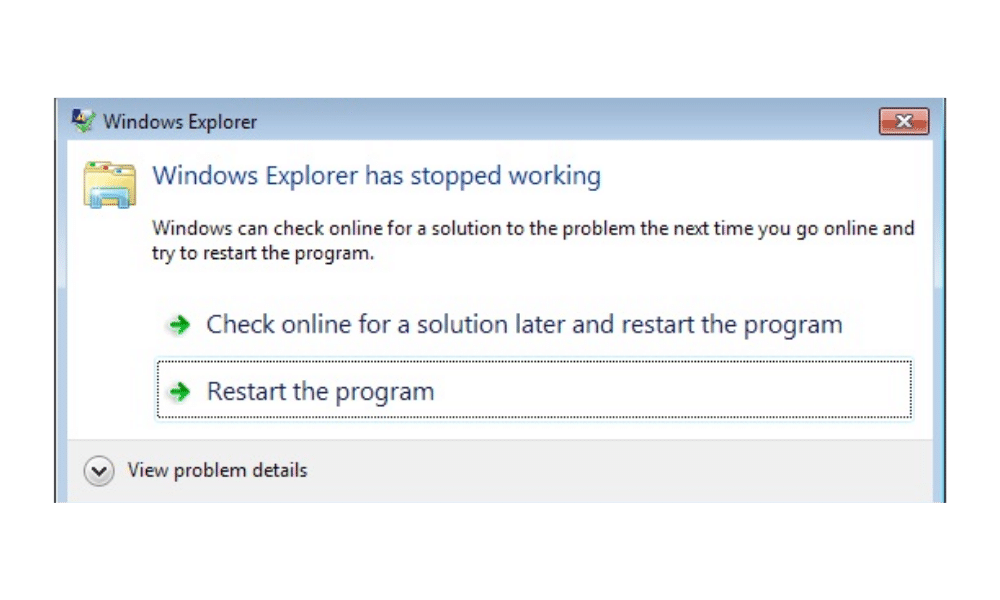
A. Identify Common Causes
Windows Explorer crashes can stem from several underlying issues. Understanding these common causes can help you diagnose and fix the problem effectively:
- Corrupted Files: System files may become corrupted due to incomplete downloads, software conflicts, or malware infections.
- Outdated Drivers: Drivers facilitate communication between your hardware and software. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to crashes.
- System File Errors: Errors in your system files can disrupt Windows Explorer’s functionality, leading to frequent crashes.
B. Fix Windows Explorer Crashing
Follow these step-by-step methods to resolve Windows Explorer crashes:
- Restart Windows Explorer:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Find and select “Windows Explorer” in the list.
- Click on “Restart” at the bottom-right corner.
- Update Drivers:
- Press Windows + X and select “Device Manager”.
- Locate any devices with a yellow exclamation mark.
- Right-click and select “Update driver”.
- Run System File Checker (sfc/scannow):
- Press Windows + X and select “Command Prompt (Admin)”.
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Allow the scan to complete and follow any on-screen instructions.
- Check for Windows Updates:
- Press Windows + I to open Settings.
- Go to “Update & Security” and click on “Windows Update”.
- Select “Check for updates” and install any available updates.
C. Prevent Future Crashes
Implement these best practices to minimize the risk of future Windows Explorer crashes:
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and drivers updated.
- System Maintenance: Run regular disk cleanups and system scans.
- Avoid Suspicious Downloads: Download files and applications only from trusted sources to reduce the risk of malware infections.
3. Outlook Keeps Crashing

A. Understand Common Causes
When Outlook crashes, it can disrupt your workflow and cause significant frustration. Identifying the common causes can help you address the issue more effectively:
- Corrupt Add-ins: Faulty or incompatible add-ins can cause Outlook to crash frequently.
- Outdated Software: Running an outdated version of Outlook can lead to performance issues and crashes.
- Conflicting Programs: Other software installed on your computer might conflict with Outlook, causing it to crash.
B. Resolve Outlook Crashing
Use these step-by-step methods to fix Outlook crashes:
- Start Outlook in Safe Mode:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type outlook.exe /safe and press Enter.
- If Outlook runs smoothly in Safe Mode, an add-in is likely causing the problem.
- Disable Add-ins:
- Go to “File” > “Options” > “Add-ins”.
- Select “COM Add-ins” and click “Go”.
- Uncheck all add-ins and click “OK”.
- Restart Outlook and enable add-ins one by one to identify the culprit.
- Update or Repair Office Installation:
- Go to “Control Panel” > “Programs” > “Programs and Features”.
- Select Microsoft Office and click “Change”.
- Choose “Quick Repair” or “Online Repair” and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Create a New Outlook Profile:
- Go to “Control Panel” > “Mail” > “Show Profiles”.
- Click “Add” to create a new profile and configure it with your email account.
- Set the new profile as the default and restart Outlook.
C. Prevent Future Crashes
Follow these best practices to avoid future Outlook errors and crashes:
- Regular Software Updates: Keep Outlook and all associated software up to date.
- Manage Add-ins: Regularly review and manage add-ins to ensure compatibility.
- Check for Conflicts: Be aware of other software installed on your computer that may conflict with Outlook. Use compatibility mode if necessary.
4. Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)

A. Understand BSOD
Encountering the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) can be alarming, but understanding its causes can help you address the issue effectively:
- Common Error Codes: BSOD often displays error codes that can provide clues about the problem. Some common codes include IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL, PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA, and CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED.
- Hardware vs. Software Issues: BSOD can result from both hardware and software problems. Identifying the source is crucial for finding the right solution.
B. Fix Blue Screen of Death
Use these methods to troubleshoot and resolve BSOD:
- Check for Hardware Issues:
- Ensure all internal components, such as RAM and hard drives, are securely connected.
- Run hardware diagnostics tools provided by your computer’s manufacturer.
- Update Drivers:
- Press Windows + X and select “Device Manager”.
- Identify any devices with a yellow exclamation mark.
- Right-click and choose “Update driver”.
- Run System Diagnostics:
- Use built-in tools like Windows Memory Diagnostic to check for memory issues.
- Press Windows + R, type mdsched.exe, and press Enter. Follow the instructions to restart and test your memory.
- Use System Restore:
- Press Windows + S and type “System Restore”.
- Select “Create a restore point” and click “System Restore”.
- Follow the prompts to restore your system to a point before the BSOD occurred.
C. Clarify the Death of Blue Screen Myth
Debunk the myths surrounding the term “Death of Blue Screen”:
- Explanation: The term “Death of Blue Screen” is often misunderstood. It implies a permanent resolution to BSOD issues, which isn’t always accurate.
- Facts vs. Fiction: While many steps can prevent BSOD, new hardware or software issues can still cause it. Staying informed and maintaining your system are key to minimizing occurrences.
By understanding BSOD, applying effective fixes, and debunking myths, you can better manage and prevent these disruptive errors, ensuring a smoother computing experience.
5. How to Fix Blue Screen of Death (Detailed Guide)
A. Take Immediate Actions
When you encounter a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), follow these immediate steps to address the issue:
- Restart Your Computer:
- Press the power button to turn off your computer.
- Wait a few seconds, then press the power button again to restart.
- Note the Error Code:
- Write down the error code displayed on the BSOD screen. This code can provide valuable information for troubleshooting.
- Disconnect External Devices:
- Remove any external devices such as USB drives, external hard drives, or printers. Restart your computer to see if the issue persists.
B. Implement In-depth Solutions
If the BSOD continues to occur, use these advanced troubleshooting methods:
- Memory Dump Analysis:
- Configure your computer to create a memory dump file when BSOD occurs.
- Use tools like WinDbg or BlueScreenView to analyze the memory dump file and identify the cause of the crash.
- Check System Logs:
- Press Windows + X and select “Event Viewer”.
- Navigate to “Windows Logs” > “System” to review critical errors and warnings around the time of the BSOD.
- Update BIOS/UEFI:
- Visit your computer manufacturer’s website to download the latest BIOS/UEFI firmware.
- Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to update the BIOS/UEFI safely.
- Run Advanced System Diagnostics:
- Use tools like Windows Performance Monitor or third-party diagnostic tools to perform a thorough check of your system’s hardware and software.
C. Prevent Future BSOD
Implement these long-term solutions to minimize the risk of BSOD:
- Regular Maintenance:
- Schedule regular system maintenance, including disk cleanup, defragmentation, and malware scans.
- Hardware Checks:
- Periodically inspect and test your hardware components. Replace or repair any faulty hardware immediately.
- Software Updates:
- Keep your operating system, drivers, and installed software up to date to ensure compatibility and stability.
By taking immediate actions, applying in-depth solutions, and following preventive measures, you can effectively address and minimize the occurrence of the Blue Screen of Death, ensuring a more reliable and stable computing experience.
6. Conclusion
Addressing issues like Windows Explorer crashes, Outlook crashes, and the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) can significantly improve your computing experience. By understanding the common causes and following the step-by-step solutions provided, you can troubleshoot and resolve these problems effectively.
However, if the above solutions do not resolve your issues, consider getting in touch with Hire IT Expert or computer professionals. They can provide advanced diagnostics and repairs to ensure your system runs smoothly.
Reinstall Windows
As a last resort, you might need to reinstall Windows to resolve persistent issues. Follow these steps to reinstall Windows:
- Backup Your Data:
- Ensure you back up all your important files and data to an external drive or cloud storage.
- Create a Windows Installation Media:
- Download the Windows Media Creation Tool from the Microsoft website.
- Use the tool to create a bootable USB drive or DVD with the Windows installation files.
- Reinstall Windows:
- Insert the installation media and restart your computer.
- Press the appropriate key to enter the boot menu (usually F2, F12, Esc, or Del).
- Select the installation media and follow the on-screen instructions to reinstall Windows.
- Restore Your Data:
- After reinstalling Windows, restore your backed-up files and reinstall your essential software.
By following these guidelines, you can address and prevent technical issues, ensuring a smoother and more reliable computing experience. Remember, seeking professional help is always an option if you encounter persistent or complex problems.
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Windows Explorer can crash due to corrupted files, outdated drivers, or system file errors. Identifying the exact cause can help you apply the correct fix.
To stop Outlook from crashing, you can start it in Safe Mode, disable problematic add-ins, update or repair your Office installation, or create a new Outlook profile.
BSOD can be caused by hardware issues, driver problems, or system errors. Common error codes displayed on the BSOD can help identify the specific cause.
You can fix BSOD by checking for hardware issues, updating drivers, running system diagnostics, and using System Restore. For detailed solutions, refer to the step-by-step guide provided in this blog.
Yes, you can prevent future crashes by keeping your system and drivers updated, performing regular maintenance, managing add-ins, and avoiding suspicious downloads.
If the provided solutions don’t work, consider contacting IT experts or computer professionals for advanced diagnostics and repair. As a last resort, you can also reinstall Windows to resolve persistent issues.
To reinstall Windows, back up your data, create a Windows installation media, and follow the on-screen instructions to perform a clean installation. After reinstalling, restore your data and reinstall necessary software.
These FAQs address common concerns and provide quick answers to help you resolve issues related to Windows Explorer, Outlook, and the Blue Screen of Death. For more detailed information, refer to the respective sections of this blog.
9. References and Resources
Websites:
- Microsoft Support: https://support.microsoft.com/
- How-To Geek: https://www.howtogeek.com/
- PCWorld: https://www.pcworld.com/
Tools and Software:
- WinDbg: Debugging tool for Windows. https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/debugger/
- BlueScreenView: Utility to analyze BSOD crash dump files. https://www.nirsoft.net/utils/blue_screen_view.html